Iodine And Lithium Ionic Compound
 __ Li+__ I− | |
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| CAS Number |
|
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.735 |
| PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| InChI
| |
| SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemic formula | LiI |
| Molar mass | 133.85 thou/mol |
| Appearance | White crystalline solid |
| Density | 4.076 k/cm3 (anhydrous) 3.494 g/cmiii (trihydrate) |
| Melting indicate | 469 °C (876 °F; 742 K) |
| Boiling bespeak | 1,171 °C (two,140 °F; one,444 K) |
| Solubility in water | 1510 g/L (0 °C) 1670 yard/Fifty (25 °C) 4330 thou/Fifty (100 °C) [1] |
| Solubility | soluble in ethanol, propanol, ethanediol, ammonia |
| Solubility in methanol | 3430 m/L (20 °C) |
| Solubility in acetone | 426 1000/L (18 °C) |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | −l.0·x−6 cm3/mol |
| Refractive index (n D) | 1.955 |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Heat capacity (C) | 0.381 J/g K or 54.4 J/mol K |
| Std molar | 75.seven J/mol K |
| Std enthalpy of | -2.02 kJ/g or −270.48 kJ/mol |
| Gibbs free energy (Δf G ⦵) | -266.9 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | 2 0 0 |
| Wink betoken | Non-flammable |
| Safety data canvass (SDS) | External MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions | Lithium fluoride Lithium chloride Lithium bromide Lithium astatide |
| Other cations | Sodium iodide Potassium iodide Rubidium iodide Caesium iodide Francium iodide |
| Except where otherwise noted, information are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
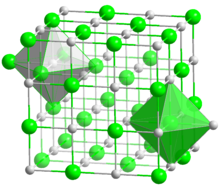
Lithium iodide, or LiI, is a chemical compound of lithium and iodine. When exposed to air, it becomes yellow in color, due to the oxidation of iodide to iodine.[2] Information technology crystallizes in the NaCl motif.[3] It tin participate in diverse hydrates.[four]
Applications [edit]

Lithium iodide is used as a solid-state electrolyte for high-temperature batteries. Information technology is too the standard electrolyte in artificial pacemakers[6] due to the long bicycle life it enables.[7] The solid is used as a phosphor for neutron detection.[viii] It is also used, in a complex with Iodine, in the electrolyte of dye-sensitized solar cells.
In organic synthesis, LiI is useful for cleaving C-O bonds. For example, it can be used to catechumen methyl esters to carboxylic acids:[9]
- RCO2CHiii + LiI → RCOtwoLi + CH3I
Similar reactions utilize to epoxides and aziridines.
Lithium iodide was used as a radiocontrast agent for CT scans. Its use was discontinued due to renal toxicity. Inorganic iodine solutions suffered from hyperosmolarity and high viscosities. Current iodinated contrast agents are organoiodine compounds.[x]
See also [edit]
- Lithium battery
References [edit]
- ^ Patnaik, Pradyot (2002) Handbook of Inorganic Chemicals. McGraw-Loma, ISBN 0-07-049439-eight
- ^ "Lithium iodide" (PDF). ESPI Corp. MSDS. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2008-03-09. Retrieved 2005-09-16 .
- ^ Wells, A.F. (1984) Structural Inorganic Chemical science, Oxford: Clarendon Printing. ISBN 0-nineteen-855370-half-dozen.
- ^ Wietelmann, Ulrich and Bauer, Richard J. (2005) "Lithium and Lithium Compounds" in Ullmann'southward Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemical science, Wiley-VCH: Weinheim. doi:x.1002/14356007.a15_393.
- ^ Senga, Ryosuke; Suenaga, Kazu (2015). "Single-atom electron free energy loss spectroscopy of light elements". Nature Communications. 6: 7943. Bibcode:2015NatCo...6.7943S. doi:x.1038/ncomms8943. PMC4532884. PMID 26228378.
- ^ Holmes, C. (2007-09-28). "The Lithium/Iodine-Polyvinylpyridine Pacemaker Battery - 35 years of Successful Clinical Use". ECS Transactions. half-dozen (five): i–7. Bibcode:2007ECSTr...6e...1H. doi:ten.1149/1.2790382. ISSN 1938-5862. S2CID 138189063.
- ^ Hanif, Maryam (2008). "The Pacemaker Battery - Review Commodity". UIC Bioengineering Student Journal.
- ^ Nicholson, K. P.; et al. (1955). "Some lithium iodide phosphors for slow neutron detection". Br. J. Appl. Phys. six (3): 104–106. Bibcode:1955BJAP....half-dozen..104N. doi:x.1088/0508-3443/6/3/311.
- ^ Charette, André B.; Barbay, J. Kent and He, Wei (2005) "Lithium Iodide" in Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis, John Wiley & Sons. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rl121.pub2
- ^ Lusic, Hrvoje; Grinstaff, Mark W. (2013). "X-ray-Computed Tomography Contrast Agents". Chemic Reviews. 113 (3): 1641–66. doi:10.1021/cr200358s. PMC3878741. PMID 23210836.
External links [edit]
- "WebElements – Lithium Iodide". Retrieved 2005-09-xvi .
- "Composition of Lithium Iodide – NIST". Retrieved 2006-02-03 .
Iodine And Lithium Ionic Compound,
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lithium_iodide#:~:text=Lithium%20iodide%2C%20or%20LiI%2C%20is,compound%20of%20lithium%20and%20iodine.
Posted by: scottoted1938.blogspot.com



0 Response to "Iodine And Lithium Ionic Compound"
Post a Comment